Parler
Parler Gab
Gab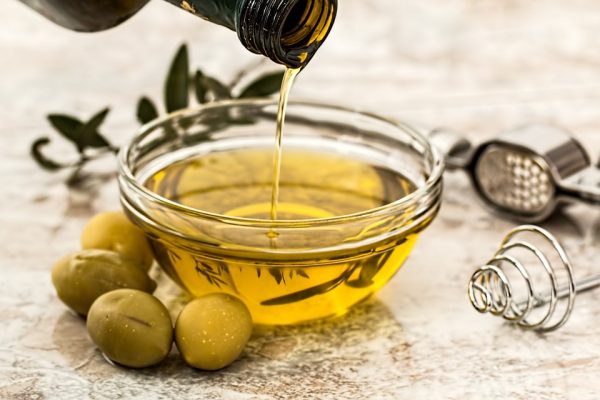
- Olive oil, particularly extra-virgin (EVOO), is high in monounsaturated fats (oleic acid) and polyphenols that can reduce inflammation, improve heart health and combat oxidative stress.
- Studies link olive oil to lower risks of heart disease, stroke, depression, breast cancer and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's due to its antioxidant properties.
- Cold-pressed organic EVOO retains the most nutrients; avoid refined or adulterated oils (mixed with cheaper oils like soybean). Store in opaque containers to prevent light damage.
- EVOO can handle moderate heat (up to 375 F) but is best for low-heat cooking, dressings and finishing dishes. Avoid high-heat frying to preserve antioxidants.
- Non-organic olive oil may contain pesticides (like glyphosate) or heavy metals. Organic certification ensures cleaner, toxin-free production for maximum health benefits.
History and origin of olive oil
Olive oil is derived from the fruit of the olive tree (Olea europaea), primarily cultivated in the Mediterranean basin. Spain, Italy, Greece and Turkey dominate global olive oil production. Its use dates back over 6,000 years, with evidence of olive oil extraction found in ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt. The Greeks and Romans valued it for cooking, skincare and even religious ceremonies. Today, olive oil has become a global commodity, particularly after World War II, when researchers identified the "Mediterranean Diet" as one of the healthiest eating patterns in the world. Extra virgin olive oil, the least processed form, is now a dietary mainstay for health-conscious consumers.Nutritional profile and health benefits
Olive oil's health benefits stem from its impressive nutrient composition:Healthy fats (monounsaturated fatty acids - MUFAs)
- Primarily oleic acid, which reduces inflammation and supports heart health.
- Helps lower LDL ("bad") cholesterol while increasing HDL ("good") cholesterol.
Antioxidants (polyphenols and vitamin E)
- Polyphenols such as oleocanthal (with anti-inflammatory effects similar to ibuprofen) and hydroxytyrosol fight oxidative stress.
- Vitamin E protects cells from free radical damage, promoting skin and immune health.
Other beneficial compounds
- Squalene – A natural compound that may help prevent cancer and support skin hydration.
- Phytosterols – Plant compounds that help block cholesterol absorption in the gut.
Why choose organic
Choosing high-quality organic olive oil helps avoid harmful pesticides and contaminants. While olives naturally require fewer pesticides than crops like celery, peaches or strawberries (which can contain 47–67 pesticides per serving), conventional olive farming may still use neurotoxic chemicals like chlorpyrifos and glyphosate, linked to Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Organic certification ensures no synthetic pesticides are used. Additionally, some olive oils may contain traces of heavy metals like lead or arsenic from soil contamination, so reputable producers test for these. For the safest and healthiest option, opt for cold-pressed, extra virgin, organic olive oil.Culinary uses of olive oil
Olive oil's versatility shines in countless recipes. Here are some classic and modern ways to use it:Dressings and dips
- Traditional Greek salad dressing (olive oil, lemon juice, oregano)
- Hummus (blended with chickpeas and tahini)
- Bruschetta topping (olive oil, tomatoes, garlic, basil)
Cooking and sautéing
- Sautéed greens (spinach, kale or Swiss chard)
- Roasted vegetables (drizzled before baking)
Baking and frying
- Olive oil cakes (a moist, Mediterranean-style dessert)
- Light frying (for dishes like falafel or fish)
Finishing touches
- Drizzled over soups (like gazpacho) or pasta
- Bread dipping oil (mixed with herbs and balsamic vinegar)
More related stories:
Olive oil really is the healthiest oil for frying foods, scientists find.
How extra virgin olive oil protects against Alzheimer's.
Olive oil helps prevent visible facial skin aging.
Sources include: Brighteon.AI NaturalNews.com Brighteon.comMarshmallow Root: An ancient sweet treat with medicinal properties
By Ava Grace // Share
Millet: The ancient superfood making a modern comeback
By Laura Harris // Share
High doses of omega-3s may slow Alzheimer’s progression
By News Editors // Share
Governments continue to obscure COVID-19 vaccine data amid rising concerns over excess deaths
By patricklewis // Share
Tech giant Microsoft backs EXTINCTION with its support of carbon capture programs
By ramontomeydw // Share
Germany to resume arms exports to Israel despite repeated ceasefire violations
By isabelle // Share