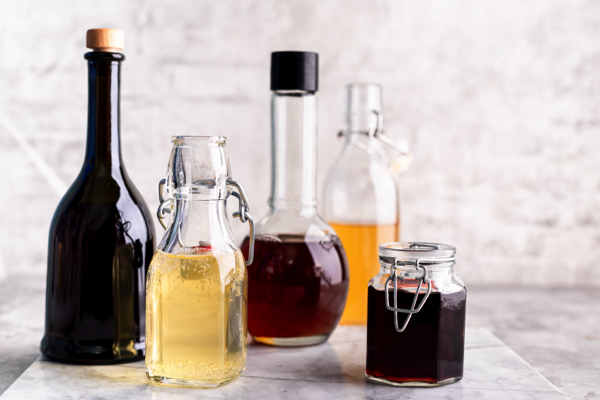
Vinegar, a staple in kitchens worldwide, has been used for thousands of years not just for culinary purposes, but also for its potential health benefits. Modern scientific research is now catching up, providing evidence for many of these traditional uses. This article explores 20 evidence-based benefits of vinegar extracted from the GreenMedInfo Vinegar Database, demonstrating its potential as a powerful addition to a healthy lifestyle.
(Article republished from
GreenMedInfo.com)
1. Blood Sugar Control
Vinegar has shown promising effects in managing blood sugar levels, particularly in individuals with
type 2 diabetes. Studies indicate that consuming vinegar with meals can significantly reduce post-meal blood glucose and insulin responses.
1
2. Weight Management
Research suggests that vinegar consumption may aid in weight loss efforts. A study found that daily vinegar intake led to reduced body weight, body fat mass, and serum triglyceride levels in obese Japanese subjects.
2
3. Heart Health
Vinegar may contribute to cardiovascular health by reducing risk factors such as
high blood pressure and
cholesterol levels. A study on rats showed that acetic acid, the main component of vinegar, lowered blood pressure through various mechanisms.
3
4. Antimicrobial Properties
Vinegar has long been used as a natural preservative and disinfectant. Scientific studies confirm its antimicrobial effects against various pathogens, including
E. coli and
Staphylococcus aureus.
4
5. Cancer-Fighting Potential
While more research is needed, some studies suggest that vinegar may have anti-tumor effects. A study on human
cancer cells showed that sugar cane vinegar induced apoptosis in leukemia cells.
5
6. Digestive Health
Vinegar may improve digestive health by increasing the acidity in the stomach, which can aid in the breakdown of food. It's also thought to have prebiotic effects, potentially supporting gut microbiome health.
6
7. Skin Health
Apple cider vinegar, in particular, has been traditionally used for skin conditions. A study found that acetic acid in apple cider vinegar was effective against Propionibacterium acnes, a bacterium involved in acne formation.
7
8. Bone Health
Vinegar consumption may support bone health. A study on mice found that vinegar intake increased calcium absorption and retention, potentially reducing the risk of
osteoporosis.
8
9. Antioxidant Properties
Many types of vinegar, especially those made from fruits, contain antioxidants. These compounds help protect the body against
oxidative stress and cellular damage.
9
10. Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Regular vinegar consumption may improve insulin sensitivity in individuals with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance. This effect can lead to better blood sugar control and metabolic health.
10
11. Appetite Suppression
Vinegar may help in weight management efforts by
increasing feelings of fullness. A study found that vinegar consumption with a high-carb meal increased satiety and led to lower calorie intake throughout the day.
11
12. Improved Nutrient Absorption
The acetic acid in vinegar may enhance the body's ability to absorb certain nutrients. For example, it's been shown to increase iron absorption from plant sources.
12
13. Reduced Inflammation
Some studies suggest that vinegar may have anti-inflammatory properties. This could have implications for various chronic diseases associated with
inflammation.
13
14. Enhanced Athletic Performance
Vinegar consumption before exercise may improve endurance. A study on mice found that acetic acid increased the animals' capacity for exercise.
14
15. Potential Neuroprotective Effects
Emerging research suggests that vinegar may have neuroprotective properties. A study on fruit fly models of
Alzheimer's disease found that apple cider vinegar reduced markers of the disease.
15
16. Improved Lipid Profile
Vinegar consumption may help improve cholesterol levels. A study on rats fed a high-cholesterol diet found that apple cider vinegar significantly reduced total cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
16
17. Enhanced Calcium Absorption
The acetic acid in vinegar may enhance calcium absorption, which is crucial for bone health. This effect has been observed in both animal and human studies.
17
18. Potential Anti-Allergic Effects
Some research suggests that vinegar may have anti-allergic properties. A study on mice found that acetic acid suppressed the production of certain inflammatory substances involved in allergic reactions.
18
19. Blood Pressure Regulation
Regular vinegar consumption may help regulate blood pressure. A study on spontaneously hypertensive rats found that acetic acid significantly reduced blood pressure.
19
20. Potential Anti-Cancer Properties
While more research is needed, some studies suggest that vinegar may have anti-cancer properties. A study on human colon cancer cells found that sugar cane vinegar induced cell death in these cancer cells.
20
How to Incorporate Vinegar into Your Diet
While the potential health benefits of vinegar are numerous, it's important to consume it safely and in moderation. Here are some guidelines and suggestions for incorporating vinegar into your diet:
1. Buy Organic: Always buy organic vinegar, with raw apple cider vinegar top of the list, when available.
2. Dilution is Key: Never consume vinegar undiluted. The high acidity can damage tooth enamel and potentially irritate your esophagus. Always dilute vinegar before consuming.
21
3. Start Small: Begin with small amounts, such as 1-2 teaspoons in a large glass of water, and gradually increase to no more than 1-2 tablespoons per day.
4. Timing Matters: For blood sugar management, consider taking vinegar before or with meals. Some studies have shown benefits from consuming vinegar about 30 minutes before a meal.
22
5. Culinary Uses: Incorporate vinegar into your diet through culinary uses:
- Use as a salad dressing
- Add to marinades for meats and vegetables
- Use in homemade pickles or preserves
- Add a splash to soups or stews for extra flavor
6. Choose the Right Type While all vinegars offer health benefits, some types may be more beneficial for specific purposes:
- Apple cider vinegar is often recommended for its potential weight loss and blood sugar control benefits
- Balsamic vinegar is high in antioxidants
- Rice vinegar may be gentler on the stomach
7. Consider a Beverage: Create a health tonic by mixing 1-2 teaspoons of vinegar (especially apple cider vinegar) in a glass of water. You can add a small amount of honey for taste if desired.
8. Be Consistent: For potential health benefits, consistency is key. Regular, moderate consumption is likely more beneficial than sporadic, large doses.
9. Mind Your Medications: If you're on medications, especially diabetes medications or diuretics, consult with your healthcare provider before adding vinegar to your diet, as it may interact with certain drugs.
23
10. Protect Your Teeth: To minimize potential damage to tooth enamel, consider drinking vinegar beverages with a straw, and rinse your mouth with plain water afterward.
11. Listen to Your Body: Everyone's body reacts differently. If you experience any adverse effects, such as nausea or acid reflux, reduce your intake or discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional.Remember, while vinegar can be a healthy addition to your diet, it's not a miracle cure. It should be part of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle, not a replacement for medical treatment or a nutritious diet.
Conclusion
The scientific evidence supporting the health benefits of vinegar is growing, offering exciting possibilities for this common household ingredient. From blood sugar control to potential anti-cancer properties, vinegar's diverse effects on health are impressive. However, it's important to note that while these studies are promising, more research is needed to fully understand the extent of vinegar's health benefits in humans.
Read more at:
GreenMedInfo.com
 Parler
Parler Gab
Gab